In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Epistasis 2. Inhibitory gene 3. Complementary Gene 4. Duplicate Genes 5. Additive Gene effect 6. Supplementary gene or Recessive Epistasis
(ii) Non allelic interaction/Intergenic interaction
When interaction takes place between non allele is called non allelic gene interaction. It changes or modifies other non allelic gene.
Examples of nonallelic interaction.
1. Epistasis :-
When, a gene prevents the expression of another non-allelic gene, then it is known as epistatic gene and this phenomenon is known as Epistasis.
Gene which inhibit the expression of another non alleleic gene is called epistatic gene and expression of gene which is suppressed by epistatic gene called hypostatic gene.
Example :-
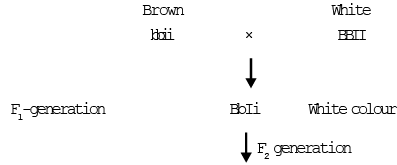
Hair Colour in Dog :-
B = Dominant allele for black colour of hairs.
b = Recessive allele for brown colour of hairs.
I = Epistatic gene.
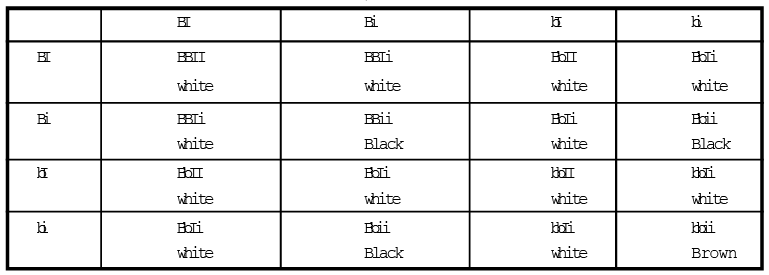
If the genotype bbii for brown colour and BBII for white colour.
Following types of generation will be obtained by following crosses.
It is obviously clear by above analysis, the phenotypic ratio of F2 - generation in epistasis is - 12:3:1
2. Inhibitory gene
Inhibitory gene itself have no phenotype but inhibits the effect of other non allelic gene. Non allelic gene behaves as recessive. * Inhibitory gene must be in dominant stage & inhibit the effect of only dominant gene.
Ex., Leaf colour in Rice
R – Purple
r – Green
I – Inhibitory gene
R – I – Green – 9
R – ii – Purple – 3
rr – I – Green – 3
rr – ii – Green – 1
13 (Green) : 3(Purple)
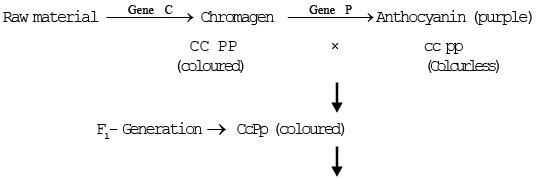
3. Complementary Gene :-
Two pair of non allelic genes are essential in doninant form to produce a particular character.
Such genes that act together to produce an effect that neither can produce, it's effect separately are called complementary genes.
Both types of gene must be present in dominant form.
Example :- Colour of flowers in Lathyrus odoratus :-
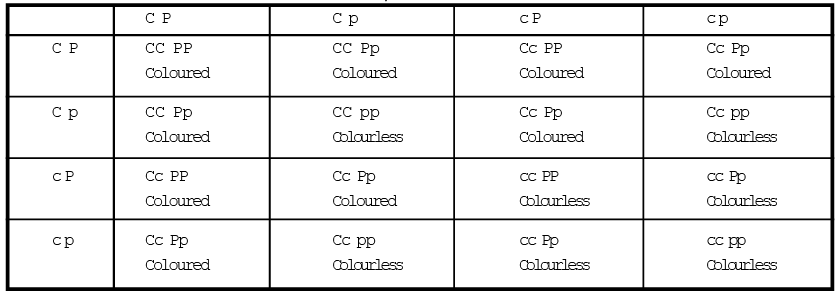
C – P Purple coloured
C – pp colour less
cc – P colour less
cc – pp colour less
Thus phenotypic ratio of complementary genes = Coloured : Colourless 9 : 7
4. Duplicate Genes :-
Two pairs of non-allelic genes require are for a character . If any one of them gene is dominant, then this character is expressed such type of gene is called duplicate gene.
Example :- Fruit shape in Capsella. Two pair of non-allelic genes are present in Capsella for triangular shape of fruits.
If any one gene out of them is dominant, the shape of fruit is triangular and no one gene is dominant than fruits will be ovaid.
If TTDD = For triangular shape
ttdd = For top shape of fruits
Phenotypic ratio of F2 -> Triangular : Top shaped 15 : 1
5. Additive Gene effect :
In additive gene effect if non allelic gene seperately in dominant stage phenotype is same but both gene come dominant stage together phenotype is change due to additive effect. eg. Fruit shape in cucumber
A – bb→ spherical
aa B→ spherical
A – B – discoid (new phenotype)
aa bb – cylinderical
6. Supplementary gene or Recessive Epistasis :-
A pair of gene change the effect of another non allelicgene, is called supplementary gene.
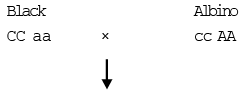
Example :- Coat colour in Mice.
If alleles, C = Black coat colour
c = Albino (Colourless coat) or (It has no effect)
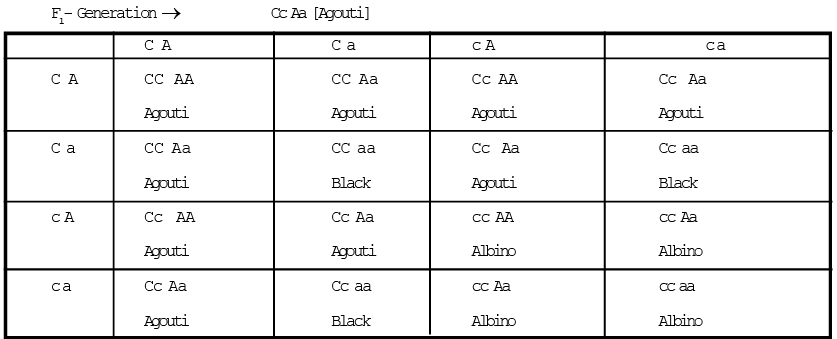
A = Supplementary geneWhen black coat mice crossed with albino mice, the F1 generation is Agouti.
It means, here the effect of non allelic gene is changed.
Thus, Recessive epistasis or supplementary gene ratio in F2 - Agouti (9) : Black (3) : Albino (4)
Gene interaction: Non allelic interaction | Genetics
![Gene interaction: Non allelic interaction | Genetics]() Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:



No comments: