In this article we will discuss about:- Cytoplosmic Inheritance and Cytoplasmic inheretance types
Inheritance of characters which are controlled by cytogene or cytoplasm is called cytoplosmic inheritance. Genes which are present in cytoplasm called 'cytogene' or 'plasmagene' or extra nuclear gene.
Total cytogene present in cytoplasm is called 'Plasmon'.
A gene which is located in the nucleus is called 'karyogene'.
- Inheritance of cytogene in organisms occurs only through the female. Because female gamete has karyoplasm, simultaneously it has cytogene because of more cytoplasm.
- The male gamete of higher plant is called male nucleus. It has very minute [equivelent to nil] cytoplasm. so male gamete only inherited karyogene.
- Thus, inheritance of cytogene occurs only through female. (also called maternal inheritance)
- If there is a reciprocal cross in this condition, then results may be effected.
Cytoplasmic inheretance are of three types :
1. Cytoplasmic inheritance involving essential organelles like, Chloroplast and mitochondria called as organellar genetics.
2. Maternal effect depending indirectly on nuclear genes and involving no known cytoplasmic hereditary unit called aspredetermination. In this maternal effect is determined before fertilization.
3. Cytoplasmic inheritance involving dispensable and infective hereditary particle in cytoplasm which may or may not depend on nuclear genes called as Dauermodification.
Example of Organellar Genetics : (True examles of cytoplasmic inheritance)
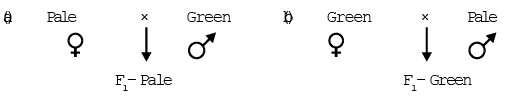
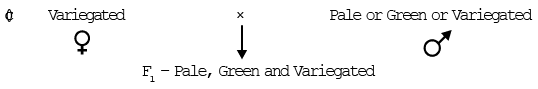
(a) Plastid inheritance in Mirabilis jalapa: cytoplasmic inheritance first discovered by Correns in Mirabilis jalapa. InMirabilis jalapa branch (leaf) colour is decided by type of plastid present in leaf cells. So it is an example of cytoplasmic inheritance.
Branch colour
(b) Male sterility in maize plant : Gene of male sterelity present in mitochondria. If a normal male plant crossed with a female plant which has genes of male sterility then all the generation of male become sterile because a particular gene was present with female which inherited by female.
(c) Albinism in plant : Gene of albinism found in chloroplast. Gene of albinism in Maize is lethal.
(d) Inheritance of Bacterial plasmid : In bacteria plasmid inheritance is due to conjugation.
(e) Petite form in yeast (mitochondrial gene) : Petite is mutant form of yeast. This mutant form is slow growing on culture medium.
(f) Iojap inheritance in Maize : Iojap is characterized by constrasting strip of green and white colour of leaves.
(g) Poky Neurospora (mitochondrial gene) : Poky is mutant form of Neurospora. It is slow growing on culture medium.
Example of predetermination
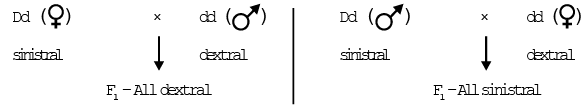
Shell coiling in snail (Limnaea peregra) In snail shell coiling can be of dextral (Coiling to the right) or sinistral (coiling to the Left). This direction of coiling is genetically controlled. The dextral coiling depends upon dominant allele 'D' and sinistral coiling depends upon recessive allele 'd'. So the dextral is DD, Dd and sinistral is dd.
Above reciprocal cross indicates that phenotype of offspring is decided by genotype of female parent not the phenotype of female parent. Even if female parent contains only one dominant gene 'D' then phenotype of all offsprings is dextral.
Example :
Example of Dauermodification -
(a) Sigma particle in Drosophila:- These particles are virus like particles which are present in Drosophila and related to CO2 sensitivity. Inheritance of sigma particle takes place through the egg cytoplasm.
(b) Kappa particle in Paramecium:- Kappa particles are found in certain "Killer strains" of Paramecium and are responsible for production of substance paramecin which is toxic to strain not prossessing Kappa. (Sensitive Strain) The minimum number of kappa particles is required 400 to secrete paramecin. Kappa particles are symbiotic bacteria named "Caedobacter taeniospiralis".
Genetics: Cytoplosmic Inheritance and Types | Genetics
 Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:


No comments: