In this article we will discuss about:- Allelic interaction or Intragenic interaction
GENE INTERACTION
Gene interaction is two types :
(i) Allelic interaction/Intragenic interaction
(ii) Non allelic interaction/Intergenic interaction
i) Allelic interaction or Intragenic interaction
Allelic interaction takes place between allele of same gene which are present at same locus.
Example of Allelic interaction are as follows :–
[1] Incomplete dominance :-
According to Mendel's law of dominance, dominant character must be present in F1 generation. But in some organisms, F1 generation is different from the both parents.
Both factors such as dominant and recessive are present in incomplete dominance but dominant factors is unable to express its character completely, resulting Intermediate type of generation is formed which is different from the both parents. Some examples are –
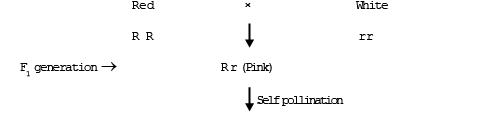
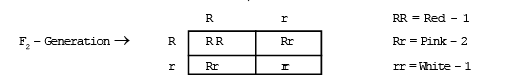
(a) Flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa : Incomplete dominance was first discovered by Correns in Mirabilis jalapa. This plant is called as '4 O' clock plant 'or'Gul-e-Bans'. Three different types of plant are found in Mirabilis on the basis of flower colour, such as red , white and pink. & When plants with red flowers is crossed with white flower, plants with pink flower obtained in F1 generation. The reason of this is that the genes of red colour is incompletely dominant over the genes of white colour. & When, F1 generation of pink flower is self pollinated then the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation is red, pink, white is 1:2:1 ratio in place of normal monohybrid cross ratio 3:1. & The ratio of phenotype and genotype of F2 generation in incomplete dominance is always same.
(b) Flower colour in Antirrhinum majus :- Incomplete dominance is also seen in flower colour of this plant.This plant is also known as 'Snapdragon ' or 'Dog flower'. Incomplete dominance is found in this plant which is the same as Mirabilis.
(c) Feather colour in Andalusian Fowls :- Incomplete dominance is present for their feather colour. When a black colour fowl is crossed with a white colour fowl, the colour of F1 generation is blue.
[2] Co-dominance :-
In this phenomenon, both the gene expressed for a particular character in F1 hybrid progeny. There is no blending of characters, wherease both the characters expressed equally.
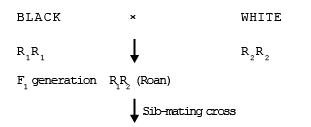
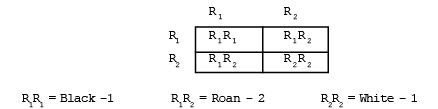
Examples :- Co-dominance is seen in animals for coat colour. when a black parent is crossed with white parent, a roan colour F1 progeny is produced.
When we obtain F2 generation from the F1 generation, the ratio of black ; black-white (Roan) ; white animals is 1 : 2 : 1
Note :- F2 generation is obtained in animals by sib-mating cross.
It is obvious by above analysis that the ratio of phenotype as well as genotype is 1:2:1 in co-dominance.
In incomplete dominance, characters are blended phenotypically, while in co-dominace, both the genes of a pair exhibit both the characters side by side and effect of both the character is independent from each other.
Other Examples of Co-dominance :
(ii) AB blood group inheritance (IAIB)
(iii) Carrier of Sickle cell anaemia (HbA HbS)
[3] Multiple allele :–
More than 2 alternative forms of same gene called as multiple allele. Multiple allele is formed due to mutation. Multile allele located on same locus of homologous chromosome.
A diploid individual contains two alleles and gamete contains one allele for a character.
Ex. Blood group - 3 alleles Coat colour in rabbit - 4 alleles
Example of multiple allele :
1. ABO blood group → ABO blood groups are determined by allele IA, allele IB, allele IO
IA = dominant
IB = dominant
IO = recessive Possible phenotypes - A, B, AB, O
2. Coat colour in rabbit → Four alleles for coat colour in rabbit
Wild type = Full coloured = agouti = C+
Himalayan [white with black tip on extremities (like nose, tail and feet)] = ch
Chinchilla [mixed coloured and white hairs] = cch
albino = Colourless = ca
These alleles show a gradient in dominance C+ > cch > ch > ca
Possible genotypes –
Coloured = C+C+, C+cch, C+ch C+ca
Chinchilla = cchcch , cchch , cchca
Himalayan = chch , chca
Albino = caca
Eye colour in Drosophila and self incompatibility genes in plants are also the example of multiple allelism.
[4] Lethal gene :–
Gene which causes death of individual in early stage when it comes in homozygous condition called lethal gene. Lethal gene may be dominant or recessive both, but mostly recessive for lethality. Many of these genes which do not cause definite lethality are called semilethals. In semilethal gene death occurs in late stage.
1. Lethal gene was discovered by L. Cuenot in coat colour of mice.
Yellow body colour(Y) was dominant over normal brown colour(y).
Gene of yellow body colour is lethal.
So homozygous yellow mice are never obtained in population. It dies in embryonal stage.
When yellow mice were crossed among themselves segregation for yellow and brown body colour was obtained in 2 : 1 ratio.
YY - death in embryonal stage modified ratio = 2 : 1
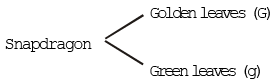
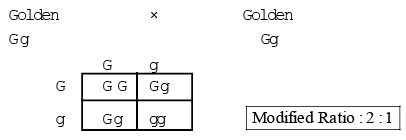
2. In plant lethal gene was first discovered by E. Baur in Snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus)
Homozygous golden leaves are never obtained.
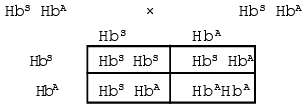
3. Sickle cell anaemia in human. In human, gene of sickle cell anaemia HbS is the example of lethal gene.
When two carrier indivudials of sickle cell anaemia are crosed then offsprings are obtained in 2 : 1 ratio.
Sublethal gene but ratio 2 : 1
[5] Pleiotropic gene :–
Gene which controls more than one character is called pleiotropic gene. This gene shows multiple phenotypic effect.
For example :
(1) In Pea plant : Single gene influences
2) In Drosophila recessive gene of vestigial wings also influence the some another characters:
Structure of reproductive organs
Longevity (Length of Body)
Bristles on wings.
Reduction in egg production.
(3) Examples of pleiotropic gene in human.
(a) Sickle cell anaemia - Gene HbSβ provide a classical example of pleiotrophy. It not only causes haemolytic anaemia but also results increased resistance to one type of malaria that caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The sickle cell HbSβ allele also has pleiotropic effect on the development of many tissues and organs such as bone, lungs, kidney, spleen, heart.
(b) Cystic fibrosis – Hereditary metabolic disorder that is controlled by a single aoutosomal recessive gene.
The gene specifies an enzyme that produces a unique glycoprotein.
This glycoprotein results in the production of mucous.
More mucous interfere with the normal functioning of several exocrine glands including those in the skin, lungs, liver and pancreas.
Gene interaction : Allelic interaction | Genetics
 Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:

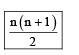

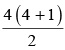

No comments: