In this article we will discuss about:- 1) Linkage Definition 2) Theory of linkage 3) Arrangement of linked Genes on Chromosomes 4) Types of Linkage 5) sex linkage 6) sex linkage Types
1) Linkage Definition
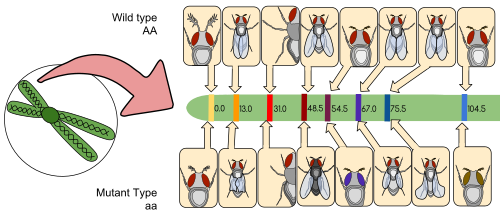
Collective inheritance of character is called linkage. Linkage first time seen byBatesonandPunnett inLathyrus odoratus and gave coupling and repulsion phenomenon. But they did not explain the phenomenon of linkage. Sex linkage was first discoverd by Morgan in Drosophila & coined the term linkage. He proposed the theory of linkage.
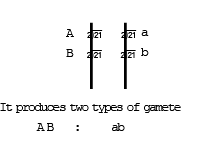
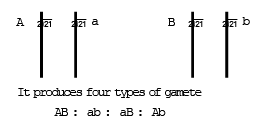
Linkage and independent assortment can be represented in dihybrid plant, as –
In case of linkage in dihybrid AaBb
In case of independent assortment in dihybrid AaBb
2) Theory of linkage
1. Linked genes are linearly located on same chromosome. They get separated if exchange (crossing over), takes place between them.
2. Strength of linkage α1/ distance between the genes . It means, if the distance between two genes is increased then strength of linkage is reduced and it proves that greater is the distance between genes, the greater is the probability of their crossing over.
Crossing over obviously disturbs or degenerates linkage. Linked genes can be separated by crossing over.
Factors affecting crossing over (C.O) :-
(1) Distance
(2) Temperature
(3) X-Ray
(4) Age
(5) Sex
3) Arrangement of linked Genes on Chromosomes :-
The arrangement of linked genes in any dihybrid plant is two types.
[a] Cis - Arrangement :- When, two dominant genes located on one chromosome and both recessive genes located on another chromosome, such type of arrangement is termed as cis-arrangement. Cis-arrangement is an original arrangement.
Two types of gamete can be produced in cis-arrangement → (AB) and (ab).
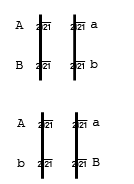
[b] Trans-arrangement :- When a chromosome bears one dominant and one recessive gene, and another chromosome also possess one dominant and one recessive gene, such type of arrangement is called trans-arrangement.Trans-arrangement is not an original form. It is due to crossing over. Two types of gamete also formed in trans-arrangement but it is different from cis-arrangement (Ab) and (aB).
3) Types of Linkage :-
There are two types of linkage
1 COMPLETE LINKAGE :- Linkage in which genes always show parental combination. It never forms new combination.
Crossing over is absent in it. Such genes are located very close on the chromosomes. Such type of linkage very rare in nature. e.g. male Drosophila, female silk moth.
2. INCOMPLETE LINKAGE :- When new combinations also appear along with parental combination in offsprings, this type of linkage is called incomplete linkage, the new combinations form due to crossing over. The percentage of new combination is equal to the percentage of crossing over.(<50%)
Linkage group :- All the genes which are located on one pair of homologous chromosome form one linkage group. Genes which are located on homologous chromosomes inherit together so we consider one linkage group.
Application of Linkage :-
Distance can be identified by the incomplete linkage. It's unit is centi Morgan.
Genetic map/Linkage map/chromosome map - In genetic map different genes are linearly arranged according to % of crossing over (μ Distance) between them. With the help of genetic map we can find out the position of a particular gene on chromosome. Genetic map is helpful in the study of genome.
5) Sex Linkage
When the genes are present on sex-chromosome is termed as sex linked gene and such phenomenon is known as sex-linkage. Two - types of sex linkage :
1. X-linkage.
Genes of somatic characters are found on x-chromosome. The inheritance of x-linked character may be through the males and females. e.g. Haemophilia, Colour blindness
2. Y- linkage.
The genes of somatic characters are located on Y- chromosome. The inheritance of such type of character is only through the males. Such type of character is called Holandric character. These characters
found only in male.
e.g. (1) Gene which forms TDF /sry-gene (3) Webbed toes
(2) Hypertrichosis (excessive hair on ear pinna.) (4) Porcupine skin
Gene which is located on differential region of Y - chromosome is known as Holandric gene.
Types of Inheritance of sex linked characters :-
1. Criss cross inheritance (Morgan) :- In criss-cross inheritance male or female parent transfer a X- linked character to grandson or grand daughter through the offspring of opposite sex.
(a) Diagenic (Diagynic) :- Inheritance in which characters are inherited from father to the daughter and from daughter to grandson.
Father → daughter → grand son.
(b) Diandric :- Inheritance in which characters are inherited from mother to the son and from son to grand
daughter.
Mother → Son → Grand-daughter.
(2) Non criss-cross inheritance : In this inheritance male or female parent transfer sex linked character to grand son or grand daughter through the offspring of same sex.
(a) Hologenic (Hologynic) :- Mother → Daughter → Grand-daughter (female to female)
(b) Holandric :- Father → Son → Grand-son (male to male)
Sex-Limited Character :- These characters are present in one sex and absent in another sex. But their genes are present in both the sexes and their expression is depend on sex hormone.
Example :- Secondary sexual characters → these genes located on the autosomes and these genes are present in both male and female, but effect of these are depend upon presence or absence of sex-hormones.
For example - genes of beard-moustache express their effects only in the presence of male hormone - testosterone.
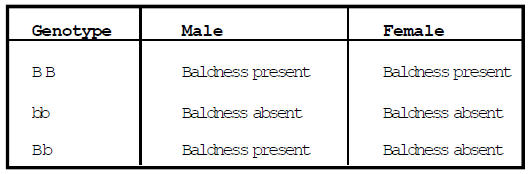
Sex Influenced Characters : - Genes of these characters are also present on autosomes but they are influenced differently in male and female. In heterozygous condition their effect is different in both the sexes.
Example :- Baldness :- Gene of baldness is dominant (B).
Gene Bb shows partiality in male and female, Baldness is found in male due to effect of this gene, but baldness is absent in female with this genotype.
Linkage: Theory of linkage and Types | Genetics
![Linkage: Theory of linkage and Types | Genetics]() Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:

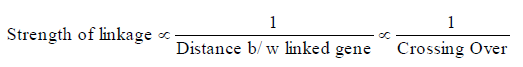
No comments: