In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Mendelism 2. Rediscovery by three scientists 3. Reason for not Recognized 4. Reasons for Mendel's success 5.Technique of Mendel
1. Mendelism
Experiments performed by Mendel on genetics and description of mechanisms of hereditory processes and formulation of principles are known as Mendelism.
Mendel postulated various experimental laws in relation of genetics.
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822 - 1884) :- Mendel was born on July 22,1822 at Heinzendorf in Austria at Silesia village. Mendel worked in Augustinian Monastery as monk at Brunn city, Austria.
In 1856-57, he started his historical experiments of heredity on pea (Pisum sativum) plant. His experimental work continued on pea plant till 1865 (19th century).
The results of his experiments were published in the science journal, "Nature For schender varein" in 1866.
This journal was in Germen language. Title was "verschue uber Pflangen Hybridan".
This journal was published by 'Natural History society of Bruno'.
A paper of Mendel by the name of "Experiment in plant Hybridization" published in this journal.
Mendel was unable to get any popularity. No one understood of him. He died in 1884 without getting any credit of his work (due to kidney disease (Bright disease) After 16 years of Mendel's death in 1900, Mendel's postulates were rediscovered.
2. Rediscovery by three scientists independently.
1. Carl Correns - Germany - (Experiment on Maize)
2. Hugo deVries (Holland) (Experiment on Evening Primerose) He republished the Mendel's results in 1901 in Flora magazine
3. Erich von Tschermak Seysenegg - (Austria) (Experiment on different flowering plants)
The credit of rediscovery of Mendelism goes to three scientists.
Correns gave two laws of Mendelism.
Law of Heredity/Inheritance/Mendelism
Ist Law - Law of segregation.
IInd Law - Law of independent assortment.
Mendel experiments remain hidden for 34 years.
3. Reason for not Recognized
1. At that time Darwin's book "Origin of Species" published. Scientists were busy in discussion with this book.
2. Mendel's ideas were ahead of that time.
3. Mendel used higher statistical calculation in his experiments so the results were complicated to understand.
4. Mendel also performed his experiments on Hieraceum plant on suggestion of Karl Nageli but Mendel did not get succeed because in Heiracium, Parthenogenesis is present.
4. Reasons for Mendel's success
1. Mendel studied the inheretance of one or two characters at a time unlike his predecessors who had considered many characters at a time. (Kolreuter-Tobacco plant, John Goss & Knight -Pea plant).
2. Selection of Material - Selection of garden Pea plant is suitable for studies ;which have the following advantages :
(i) Pea plant is annual plant with short life cycle of 2-3 months so large no. of offsprings can be analysed within a
short period of time.
(ii) It has many contrasting traits.
(iii) Natural self pollination is present in pea plant.
(iv) Cross pollination can be performed in it artificially so hybridization can be made possible.
(v) Pea plant easy to cultivate.
(vi) Pea seeds are large. In addition to pea, Mendel worked on rajama and honey bee.
3. Mendel quantitatively analyse the inheritance of qualitative characters.
4. He maintained the statistical records of all the experiments.
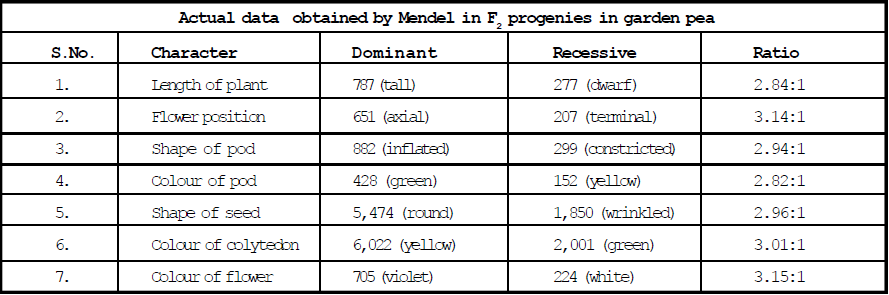
Mendel's work : Mendel studied 7 characters or 7 pairs of contrasting traits.
Average of all traits studied 2.98: (= 3:1)
In Pea plant sead coat colour and Flower colour are regulated by same gene.
Gene which controls more than one character is called as pleiotropic gene.
Mendel obtained wrinkled seeds due to absence of Starch Branching enzyme (SBE)
In Wrinkled seed free sugar is more in place of starch.
5. Technique of Mendel
- He developed a technique Emasculation and Bagging for hybridization in plants.
- Flowers of pea plant are bisexual. In this method one considered as male and another as female.
- Stamens of the plant which is used as female, are removed at juvenile stage, this is called Emasculation.
- Emasculation is done to prevent self pollination.
- Emasculated flowers covered by bags, this is called bagging.
- Bagging is only used to prevent undesirable cross pollination.
- Mature pollen grains are collected from male plants and spread over emasculated flower.
- Seeds are formed in the female flower after pollination.
- The plants that are obtained from these seeds are called First Filial generation or F1 generation according to Mendel.
- Mendel was great plant breader(true breader).
6. SOME GENETICAL TERMS
1. Factors :- Unit of heredity which is responsible for inheritance and appearance of characters.
These factors were referred as genes by Johannsen(1909). Mendel used term "element" for factor.
Morgan first used symbol to represent the factor. Dominant factors are represented by capital letter while recessive factor by small letter.
2 Allele :- Alternative forms of a gene which are located on same position [loci] on the homologous chromosome is called Allele. Term allele was coined by Bateson.
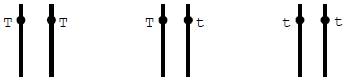
3. Homozygous :- A zygote is formed by fusion of two gametes having identicle factors is called homozygote and organism developed from this zygote is called homozygous.
Ex. TT, RR, tt
4. Heterozygous :- A zygote is formed by fusion of two different types of gamete carrying different factors is called heterozygote (Tt, Rr) and individual developed from such zygote is called heterozygous.
The term homozygous and heterozygous are coined by Bateson.
5. Hemizygous :- If individual contains only one gene of a pair then individual said to be Hemizygous. Male individual is always Hemizygous for sex linked gene.
6. Phenotype :- It is the external and morphological appearance of an organism for a particular character.
7. Genotype :- The genetic constitution or genetic make-up of an organism for a particular character.
Genotype & phenotype terms were coined by Johannsen.
8. Phenocopy :- If different genotypes are placed in different environmental conditions then they produce same phenotype. Then these genotypes are said to be Phenocopy of each other.
Genetics: Principles of Mendelian Inheritance
![Genetics: Principles of Mendelian Inheritance]() Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:


No comments: