In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Monohybrid Cross 2.Dihybrid Cross 3.Principles of Inheritance
1. MONOHYBRID CROSS
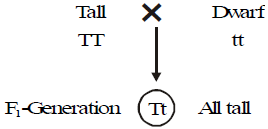
When we consider the inheritance of one character at a time in a cross this is called monohybrid cross. First of all, Mendel selected tall and dwarf plants.
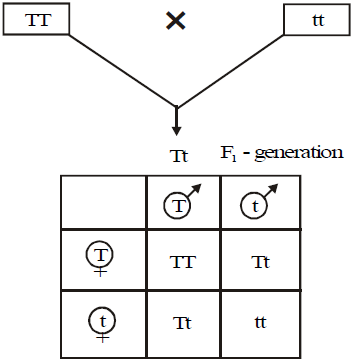
Checker Board Method :
First time, it was used by Reginald. C. Punnett (1875 - 1967)
The representation of generations to analyse in the form of symbols of squares. Male gamets lie horizontally and female gametes lie vertically.
T T = Tall (dominant homozygous),
T t = Tall (dominant heterozygous),
t t = Dwarf (recessive homozygous).
The ratio of characters (traits) appear/ visible morphologically is phenotypicratio. It is 3: 1. Genetic constitution is called Genotype [using symbols for genes] it is 1 : 2 :1
Conclusions (results) of Monohybrid Cross
Ist Conclusion (Postulate of paired factors) :
According to Mendel each genetic character is controlled by a pair of unit factor. It is known as conclusion of paired factoror unit factor.
IInd Conclusion (Postulate of Dominance):
This conclusion is based on F1 - generation. When two different unit factors are present in single individual, only one unit factor is able to express itself and known as dominant unit factor. Another unit factor fails to express is the recessive factor. In the presence of dominant unit factor recessive unit factor can not express and it is known as conclusion of dominance.
There are two exceptions of law of dominance. [A] Incomplete dominance, [B] Co-dominance,
IIIrd Conclusion (Law of segregation):
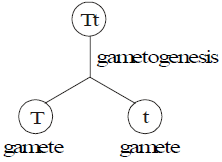
During gamete formation ; the unit factors of a pair segregate randomly and transfer inside different gamete.
Each gamete receives only one factor of a pair; so gametes are pure for a particular trait. It is known as conclusion of purity of gametes or segregation.
There is no exception of Law of segregation. The segregation is essential during the meiotic division in all sexually reproducing organisms. (Nondisjunction may be exception of this law).
2. DIHYBRID CROSS
A cross in which study of inheritance of two pairs of contrasting traits.
Mendel wanted to observe the effect of one pair of heterozygous on other pair.
Mendel selected traits for dihybrid cross for his experiment as follows :-
[1] Colour of cotyledons→ Yellow (Y) & Green (y)
[2] Seed form → Round (R) and Wrinkled (r) yellow and round characters are dominant and green and wrinkled are recessive characters.
Mendel crossed, yellow and round seeded plants with green and wrinkled seeded plants.
All the plants in F1–generation had yellow and round seeds.
When F1 plants were self pollinated to produce four kinds of plants in F2 generation such as yellow round, yellow–wrinkled, green round and green wrinkled, there were in the ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. This ratio is known as dihybrid ratio.
Expression of yellow round (9) and green wrinkled (1) traits shows as their parental combination.
Green Round and yellow wrinkled type of plants are produced by the results of new combination.
Demonstration by checker board method :-
F2 - Generation:
Phenotype :-
Yellow Round = 9/16
Yellow Wrinkled = 3/16
Green Round = 3/16
Green Wrinkled = 1/16
Thus, Phenotypic Ratio = 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
Genotype:-
Homozygous yellow & Homozygous Round – YY RR = 1
Homozygous yellow & Heterozygous Round – YY Rr = 2
Heterozygous yellow & Homozygous Round – Yy RR = 2
Heterozygous yellow & Heterozygous Round – Yy Rr = 4
Homozygous yellow & Homozygous wrinkled – YY rr = 1
Heterozygous yellow & Homozygous wrinkled – Yy rr = 2
Homozygous green & Homozygous Round – yy RR = 1
Homozygous green & Heterozygous Round – yy Rr = 2
Homozygous green & Homozygous wrinkled – yy rr = 1
Thus, Genotypic Ratio = 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1
Conclusion (Law of Independent Assortment):
The F2 generation plant produce two new phenotypes, so inheritance of seed colour is independent from the inheritance of shape of seed. Otherwise it can not possible to obtain yellow wrinkled and green round type of seeds.
This observation leads to the Mendel's conclusion that different type of characters present in plants assorted independently during inheritance.
This is known as Conclusion of Independent Assortment. It is based on F2 - generation of dihybrid cross.
The nonhomologous chromosome show random distribution during anaphase-I of meiosis.
The F2 generation plant produce two new phenotypes, so inheritance of seed colour is independent from the inheritance of shape of seed. Otherwise it can not possible to obtain yellow wrinkled and green round type of seeds.
This observation leads to the Mendel's conclusion that different type of characters present in plants assorted independently during inheritance.
This is known as Conclusion of Independent Assortment. It is based on F2 - generation of dihybrid cross.
The nonhomologous chromosome show random distribution during anaphase-I of meiosis.
Genetics: Monohybrid Cross and Dihybrid Cross
![Genetics: Monohybrid Cross and Dihybrid Cross]() Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Rajkumar
on
February 16, 2019
Rating:


No comments: